Exploring Animal Cell Structure: Biologycorner Com Animal Cell Coloring
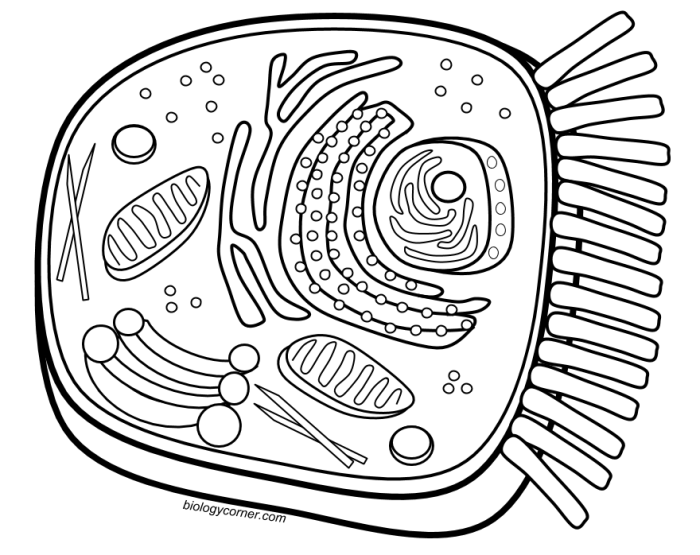
Biologycorner com animal cell coloring – Animal cells are the fundamental units of life in animals, performing a vast array of functions that contribute to the organism’s survival. Understanding the structure of these cells is crucial to comprehending how these functions are carried out. Each organelle within the animal cell plays a specific role, working in concert to maintain the cell’s life and contribute to the overall function of the organism.The animal cell is a complex and dynamic environment enclosed by a flexible plasma membrane.
This membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of substances into and out of the cell. Within the cell, a variety of organelles, each with its own specialized function, are suspended in a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm. These organelles work together in a highly coordinated manner to carry out essential life processes.
Key Organelles and Their Functions
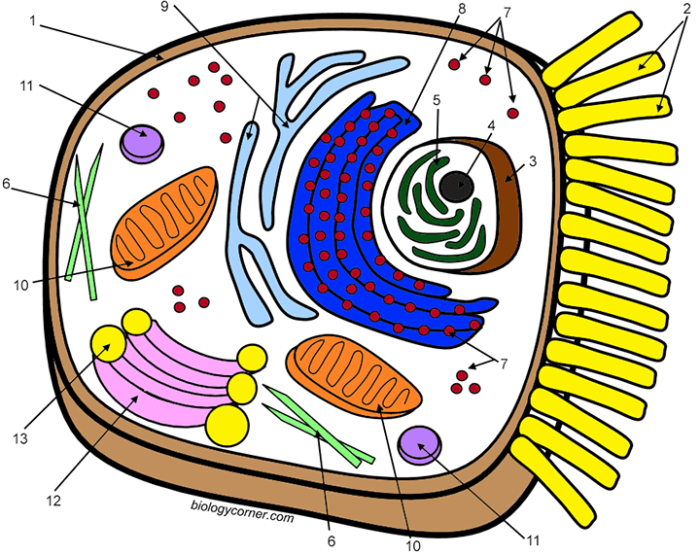
Several key organelles contribute to the overall function of the animal cell. These include the nucleus, the control center of the cell; the mitochondria, the powerhouses responsible for energy production; the ribosomes, the protein synthesis machinery; and the endoplasmic reticulum, involved in protein folding and lipid synthesis. Each organelle plays a critical role in maintaining the cell’s health and enabling it to perform its designated tasks.
| Organelle Name | Primary Function | Role in the Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Houses and protects genetic material (DNA) | Controls cell activities, including growth and reproduction, by regulating gene expression. |
| Mitochondria | Generates energy (ATP) through cellular respiration | Provides the cell with the energy needed to carry out its various functions. This process involves breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen. |
| Ribosomes | Synthesizes proteins | Translates genetic information from mRNA into proteins, which are essential for a vast array of cellular functions. Ribosomes can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Synthesizes and modifies proteins and lipids | The rough ER, studded with ribosomes, is involved in protein synthesis and folding. The smooth ER is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification. |
Organelle Arrangement and Spatial Relationships
The organelles within an animal cell are not randomly distributed but are arranged in a specific manner that reflects their functional relationships. The nucleus, often centrally located, is surrounded by the cytoplasm, which contains the other organelles. Mitochondria are scattered throughout the cytoplasm, close to areas requiring high energy. Ribosomes are either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, which extends throughout the cell, forming a network of interconnected membranes.
This organized arrangement facilitates efficient communication and transport between different organelles, ensuring the smooth operation of the cell.Imagine the cell as a bustling factory. The nucleus is the central office, containing the blueprints (DNA) for all the products. The mitochondria are the power generators, supplying energy to the entire factory. Ribosomes are the assembly lines, constructing proteins according to the blueprints.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of conveyor belts, transporting and modifying the newly synthesized proteins. The spatial relationships between these components ensure the efficient flow of information and materials within the cellular “factory.”
Creating Engaging Learning Experiences with Animal Cells
Understanding animal cell structure and function is fundamental to biology. Engaging students beyond traditional textbook learning can significantly enhance their comprehension and retention of this complex topic. Interactive activities and exploration of real-world applications can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical understanding.
Interactive Games and Activities, Biologycorner com animal cell coloring
Interactive games and activities transform learning about animal cells into a dynamic and memorable experience. These methods cater to different learning styles and encourage active participation, fostering a deeper understanding of cell components and their roles.
- Cell City Analogy: Students can create a “Cell City” project, assigning organelles to different city departments based on their functions. For example, the nucleus becomes City Hall, the mitochondria the power plant, and the ribosomes factories producing proteins. This analogy helps students visualize the interconnectedness and purpose of each organelle.
- Organelle Bingo: Create bingo cards with organelle names or descriptions. Call out functions or characteristics, and students mark the corresponding organelle on their cards. This game reinforces the association between organelle structure and function.
- 3D Model Construction: Students can construct a 3D model of an animal cell using various materials like clay, styrofoam, or even candy. This hands-on activity allows them to visualize the spatial arrangement of organelles and their relative sizes.
Supplementary Resources
Exploring resources beyond the provided coloring page can enrich the learning experience and provide different perspectives on animal cell biology.
- Khan Academy: This platform offers free educational resources, including videos and interactive exercises on cell biology, covering topics from basic organelle function to complex cellular processes.
- Cells Alive!: This website provides interactive animations and simulations of cellular processes, allowing students to visualize dynamic events like cell division and protein synthesis.
- National Geographic: National Geographic offers articles, videos, and images related to cell biology, often presenting the information within a broader biological context, such as animal physiology or disease.
Real-World Applications of Animal Cell Biology
Animal cell biology has far-reaching implications in various fields, from medicine to biotechnology. Understanding the intricacies of animal cells is crucial for developing new treatments, technologies, and a deeper understanding of life itself.
For example, in cancer research, understanding the uncontrolled growth and division of animal cells is essential for developing targeted therapies.
In the development of vaccines, knowledge of how animal cells interact with pathogens is critical for creating effective immunization strategies.
The field of regenerative medicine relies heavily on understanding animal cell differentiation and growth to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. Stem cell research, for instance, holds immense promise for treating a wide range of diseases.
Exploring the intricacies of cellular structures with resources like biologycorner.com’s animal cell coloring can be a great educational tool. For a change of pace, try some arctic animal coloring pages to explore a different kind of biology – the fascinating adaptations of creatures living in frigid environments. Then, return to the microscopic world and further your understanding of cell organelles with the biologycorner resources.
